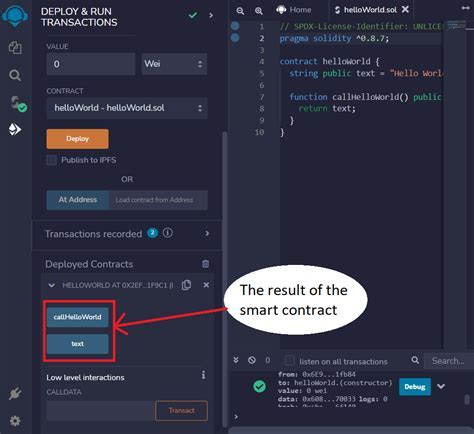
Ethereum: Complex attraction Asics
The increase in Ethereum has caused a turbulent discussion among miners, developers and experts from the industry. One of the most specific questions is the distribution of integrated circuits specific to the app (Asic) in mining pools. Some claim that great memory requirements are disturbed by Asic design, while others reject this concern as an over -response.
Asic puzzle
In order to understand why Asic, they represent the challenge of the Ethereum miners, we first define what Asics are and how they do. Asic microprocessors are made by custom designed specifically for the mining of cryptocurrencies. These chips use top graphics units (GPU) and apply their capabilities to the process of resolving complex mathematical equations, known as proof of work.
Paradox of Proof of Labor
Ethereum’s algorithm of consensus evidence of work requires a miner to resolve a high -level polynomial equation using powerful computer resources. This problem is not very difficult to break through, making it an attractive target for Asic mining hardware. As the number of miners increases, the necessary computer power increases, leading to higher energy and environmental care costs.
Problem: Great memory requirements
One of the main reasons why Asics struggles with the Ethereum algorithm of evidence is demanding demands to remember. Asic needs huge amounts of RAM (usually ranging from 256-512 GB) to store complex mathematical calculations and hash functions needed for each block. This large memory print comes at a significant price:
* Electricity Consumption
![Ethereum: ASICs and large memory requirements [duplicate]](https://www.renren1688.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/9e709e33.png)
: High energy consumption to power so expensive hardware.
* Cost : The cost of high performance, specialized computer chips can be forbidden by a set.
case against Asics
So, what stops Asic designers to simply build miners with a larger and more powerful hardware? There are several reasons:
- Design restrictions : Asics are optimized for certain tasks, not the Ethereum algorithm. The design of a miner that can handle the complex mathematical budgets required by Ethereum would require significant engineering efforts.
- Possibility : Although larger miners could be profitable in the short term, they often come with higher operational costs over time due to energy consumption and maintenance needs.
- Software Development : Creating S
The future of mining
Although it may seem like Asics retains Ethereum’s progress, the reality is tinted. As demand for mining solutions is increasing, we can expect to see progress in technology and design that will make it easier to build effective, economical miners. A constant debate over Asic is likely to launch innovations and encourage the boundaries of what is possible in the world of cryptocurrency mining.
In conclusion, while ASICs are a challenge to the Ethereum algorithm for proof of work, they are not as insurmountable as some may claim. While we continue to explore new solutions and technologies, it is clear that the future of the Criptovalut mining will form a complex factors interaction, including hardware design, software development and market demand.