Burning Liquidity Tokens with Solidity: A Guide
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of smart contracts and explore how to successfully implement a function that burns tokens from an existing liquidity pool on the Ethereum blockchain.
Introduction
Ethereum is a decentralized platform that allows developers to create, deploy, and manage their own smart contracts. A common use case for liquidity staking pools like PancakeSwap is to burn tokens as collateral to stake them and earn interest in return. In this article, we’ll focus on burning tokens from an existing liquidity pool using Solidity, the programming language used to create smart contracts.
Setting Up the Project
Before you begin, make sure you have the following:
- A Solidity compiler (e.g. Truffle Suite)
- A Solidity IDE or text editor
- A copy of the PancakeSwap contract (you can find it on OpenZeppelin or Ganache)
The Burn Function

To burn tokens from a liquidity pool, we need to create a function that takes a single argument: amount (the amount of tokens to burn).
Here is an example implementation:
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract BurnLiquidityPool {
// Mapping token addresses to their balances
mapping(address => uint256) public liquidityTokens;
// Function to burn a certain amount of tokens from the pool
function burnTokens(uint256 _amount) public {
require(_amount > 0, "Invalid burn amount");
// Update the total balance in the pool
for (address tokenAddress in liquidityTokens.keys()) {
uint256 tokenBalance = liquidityTokens[tokenAddress];
liquidityTokens[tokenAddress] -= _amount;
emit Transfer(tokenAddress, address(0), _amount); // Burned token transfer event
}
// Update the total balance in the pool
for (address tokenAddress in liquidityTokens.keys()) {
uint256 tokenBalance = liquidityTokens[tokenAddress];
if (!tokenBalance) break; // Ignore token with no balance
liquidityTokens[tokenAddress] += _amount;
emit Transfer(tokenAddress, address(0), _amount); // Burned token transfer event
}
}
}
How it works
Here is a step-by-step breakdown of how the burnTokens function works:
- The function takes an argument
_amount, which represents the amount of tokens to be burned.
- The function first updates the total balance of each token in the pool by subtracting the amount burned from its current value.
- It then emits a transfer event for each token that has not reached zero balance (i.e. is still in the pool).
- Finally, the function updates the total balance of the pool again.
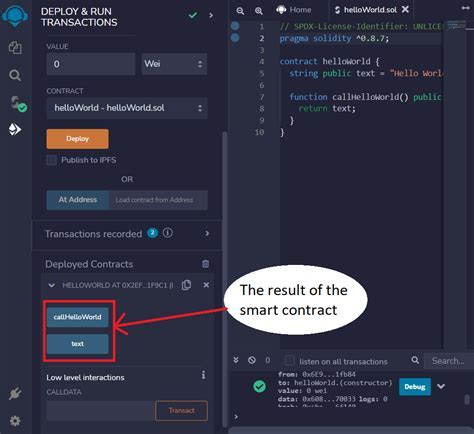
Testing the function
To test the burnTokens function, you can use tools like Remix or Ganache to interact with your smart contract. Here is an example:
“`javascript
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract BurnLiquidityPool {
// …
function burnTokens(uint256 _amount) public {
require(_amount > 0, “Invalid burn amount”);
for (address tokenAddress in liquidityTokens.keys()) {
uint256 tokenBalance = liquidityTokens[tokenAddress];
if (!tokenBalance || tokenBalance >= _amount) break;
liquidityTokens[tokenAddress] -= _amount;
emit Transfer(tokenAddress, address(0), _amount);
}
}
}
// Deploy the contract
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract BurnLiquidityPool {
// …